The rapid rise of artificial intelligence presents a dual promise and peril for the legal industry. On one hand, it offers unprecedented efficiency for tasks like document review, legal research, and contract analysis. On the other, it introduces a complex new frontier of risks surrounding client data, attorney-client privilege, and ethical compliance. Many legal professionals are struggling with a critical question: how do you properly vet these powerful new tools without exposing your firm to data breaches, AI “hallucinations,” and a growing maze of regulations?
This article is not just another list of questions. Drawing on our experience helping dozens of law firms navigate tech adoption, we have developed an actionable due diligence playbook. It is designed specifically for legal professionals to securely and ethically evaluate and adopt AI technology. This playbook will guide you through four key areas:
- Building a structured evaluation framework.
- Scrutinizing data security and confidentiality.
- Navigating compliance, ethics, and AI risk.
- Planning for practical implementation and oversight.
Establishing your legal AI evaluation framework
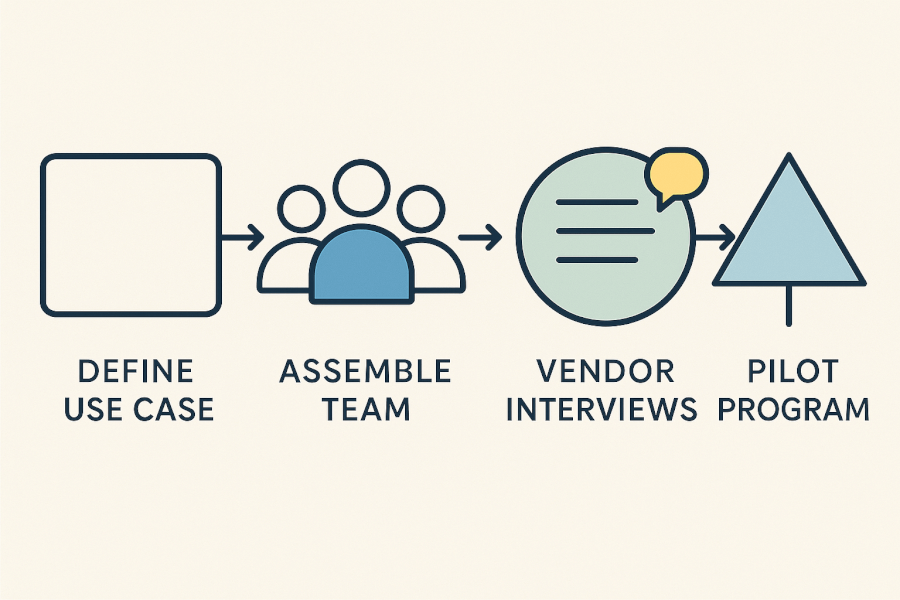
A structured, methodical approach to due diligence is essential. Ad-hoc questioning during a sales demo can lead to critical oversights. By establishing a clear framework, you ensure all key areas are examined by the right people, creating a comprehensive and defensible decision-making process. This framework consists of four distinct stages.
Stage 1: Define your use case and ROI
Before you even look at a vendor, you must look inward. The first step is to pinpoint the exact problem you are trying to solve and how you will measure success.
- What specific legal task will this AI tool solve? Be precise. Is it for first-pass document review in litigation, analyzing contracts for specific clauses, or accelerating legal research?
- How will you measure success and return on investment (ROI)? Define your key performance indicators (KPIs). These could include hours saved per case, a measurable reduction in errors, or a faster case turnaround time.
- Does the vendor’s solution directly align with this core business need? A powerful AI tool that doesn’t solve your specific problem is a distraction, not a solution.
Stage 2: Assemble your diligence team
Evaluating legal AI is not a solo task. A comprehensive assessment requires a multi-disciplinary team of stakeholders from across your firm.
- Identify key stakeholders: Your team should include representatives from IT/security, managing partners (who oversee risk), legal operations, and, most importantly, the end-user lawyers and paralegals.
- Assign specific areas of questioning: Delegate responsibility. Have your IT team lead the security and integration questions, while managing partners focus on liability and compliance. The lawyers who will use the tool should focus on usability and workflow.
Stage 3: Conduct structured vendor interviews
Use the questions in the following sections as a script to guide your vendor demonstrations and interviews. This ensures every vendor is measured against the same rigorous criteria.
- Go beyond the canned presentation: Insist on seeing live demonstrations of the product performing tasks relevant to your defined use case. If possible, use your own anonymized sample data to see how it performs in a real-world scenario.
Stage 4: Execute a pilot program
Before committing to a firm-wide rollout and a long-term contract, negotiate a limited-scope pilot program with your top one or two vendors.
- Define clear success criteria: Use the ROI metrics you defined in Stage 1 to create clear, data-driven goals for the pilot. At the end of the period, you should be able to objectively determine if the tool met its objectives.
Critical questions for data security and client confidentiality

For any law firm, the absolute foundation of due diligence is protecting client data and upholding attorney-client privilege. An efficiency gain is worthless if it comes at the cost of a data breach or a confidentiality violation. This area is non-negotiable.
Key Term: Zero-Retention Policy
A policy where the AI vendor contractually guarantees that they do not store your input prompts or data after the transaction is complete. This is a critical feature to prevent your confidential information from being used to train their models or being exposed in a potential breach of their systems.
Data handling and retention policies
- Does the vendor offer a zero-retention or “private tenant” option for our data? Can they contractually guarantee our prompts and confidential data are not used for training their models?
- Where is our data stored and processed geographically? Does this comply with data sovereignty requirements like GDPR or other client-specific needs?
- What is the certified data destruction policy for when we terminate the service? How can we verify our data has been permanently deleted?
Encryption and access control
- Is our data encrypted both in transit (using modern protocols like TLS 1.3) and at rest (using strong standards like AES-256)?
- What are the user authentication and access control mechanisms? Do they support multi-factor authentication (MFA) and granular, role-based access controls to enforce the principle of least privilege?
- Who at the vendor company can access our data and under what specific circumstances? Is every access event logged and fully auditable?
Security audits and certifications
- Can you provide a complete, recent SOC 2 Type II report for our review?
- Are you compliant with other major security frameworks, such as ISO 27001?
- How do you conduct third-party vulnerability scanning and penetration testing, and can you share a summary of the results and remediation actions?
Navigating compliance, ethics, and AI risk mitigation
For legal professionals, compliance extends beyond standard data privacy. It touches the core of professional responsibility, ethics, and mitigating new forms of technological risk. A thorough due diligence process must confront these emerging challenges head-on.
Regulatory and data protection compliance
- How does the tool help our firm comply with relevant data protection laws like GDPR, CCPA, and others?
- How is the tool classified under the EU AI Act’s risk-based approach? What is your product roadmap for ensuring ongoing compliance with this and other emerging AI-specific regulations?
- What are the terms of your Data Processing Agreement (DPA)? Does it offer adequate protection and indemnification for our firm as the data controller?
Model accuracy, bias, and hallucinations
- What specific data was the AI model trained on? How do you ensure the training data is high-quality, relevant to our legal domain, and audited for systemic biases?
- How do you measure and mitigate the risk of “hallucinations” or factually incorrect outputs? What is the model’s documented accuracy rate for the specific tasks we defined in our use case?
- What mechanisms are in place for our lawyers to report inaccuracies, biased outputs, or other model performance issues?
Liability and intellectual property
- Who is contractually liable for damages caused by an incorrect AI-generated output that our firm relies upon? What does the vendor’s liability cap look like in the service agreement?
- Who owns the output generated by the AI using our inputs and prompts? How does the vendor’s policy impact our firm’s ownership of its work product and intellectual property?
Assessing practical implementation and human oversight
An AI tool is only valuable if it can be seamlessly and safely integrated into your firm’s existing workflows. This final area of questioning focuses on the practical realities of adoption, from technical integration to the critical role of human supervision.
Integration and usability
- How does the tool integrate with our existing systems, such as our document management system (DMS), case management software, or e-discovery platforms? Is there a well-documented and robust API?
- What is the learning curve for our lawyers and staff? What specific training, onboarding, and ongoing support do you provide?
- How is user feedback collected and incorporated into your product development and update cycle?
The human-in-the-loop requirement
Does the tool’s workflow mandate a human review and validation step before any outputs can be finalized or used in a client matter?
How does the user interface make it easy for a lawyer to trace AI-generated claims, summaries, or conclusions back to the specific source documents or legal precedents? This traceability is a critical protocol for mitigating hallucination risks and upholding professional standards of verification. As Wolters Kluwer notes, it’s crucial to ask, “Can the system show its work?” when you evaluate your legal AI technology.
Support and vendor viability
- What are your defined support hours and guaranteed response times under the Service Level Agreement (SLA)?
- What is the vendor’s financial stability and long-term product roadmap? Are you a venture-backed startup or a profitable, established company?
- Can you provide references from other law firms of a similar size and practice area that we can speak with directly?
Your legal AI due diligence checklist in brief
- Build a framework: Don’t ask random questions. Define your use case, assemble a multi-disciplinary team, and run a structured pilot program before committing.
- Security is non-negotiable: Prioritize vendors with zero-retention policies, end-to-end encryption (AES-256 and TLS 1.3), and verifiable security audits like a SOC 2 Type II report.
- Scrutinize compliance & ethics: Go beyond standard data privacy. Ask tough questions about the EU AI Act, the model’s training data, and who holds contractual liability for AI errors.
- Mandate human oversight: The best AI tools augment expert judgment; they don’t replace it. Ensure the workflow includes a mandatory human validation step with clear traceability to sources.
Frequently asked questions about evaluating legal AI
What are the most important questions to ask about legal AI security?
Answer First: The most important questions concern data encryption standards, user access controls, and the vendor’s data retention and destruction policies. You must get a contractual guarantee on whether the vendor will use your confidential data to train their models, confirm where your data is stored geographically, and demand a recent SOC 2 Type II report as independent verification of their security controls.
How do I assess the accuracy and reliability of a legal AI tool?
Answer First: Assess accuracy by requesting the vendor’s documented accuracy rates for your specific use case and, more importantly, by running a pilot program with your own documents. Always ask what data the model was trained on. A model trained on a broad corpus of general internet data may be less reliable for nuanced legal tasks than one trained on a curated library of legal documents, case law, and statutes.
What is the training data source for a legal AI model?
Answer First: The training data source can be a mix of public web data, licensed legal databases, or proprietary data, and it is crucial to ask for specifics. You should inquire if any scraped or copyrighted data was used without a license, as this could present future legal and intellectual property risks for your firm. A reputable vendor will be transparent about their data provenance.
How does the legal AI vendor handle model updates and potential biases?
Answer First: Reputable vendors handle updates by continuously retraining models on new, relevant data and should have dedicated teams or processes to identify and mitigate algorithmic bias. Ask about their process for model version control, how they notify clients of significant model updates, and what mechanisms are in place for customers to report biased, unfair, or otherwise problematic outputs.
Making a confident decision in the age of AI
Adopting legal AI is quickly becoming essential for firms to stay competitive, but reckless adoption is one of the most significant risks a firm can take today. A rigorous, structured due diligence process is the only responsible path forward.
By using this playbook, legal professionals can move beyond the marketing hype and make informed, confident decisions. This structured approach allows you to harness the power of AI to build a more efficient practice while upholding your core duty to protect your clients, your firm, and your professional integrity.
Put This Playbook Into Action
Download our Comprehensive Vendor Evaluation Checklist. It combines all the questions from this guide into a single, actionable spreadsheet to help you compare vendors and make the right choice for your firm.